Viral and bacterial infections
Cimurro
Is’ caused by a virus that the ferret is extremely sensitive. This virus is almost always fatal for the animal. The distemper is transmitted both directly and indirectly, has an incubation period of 7-10 days, that in some strains also arrives at three weeks. Early symptoms include conjunctivitis, scolo oculare nasale and mucous, lack of appetite, and sometimes blackish stool for the presence of blood digested. Later onset fever and skin lesions: erythema, thickening and crusting of the skin of the chin and groin and pads. If you exceed this time, arise brain injury leading to death. There are no effective therapies: Once you are sure of the diagnosis, we recommend euthanasia. Instead there is an effective prevention: the vaccination against canine distemper, that includes a first injection 6-8 weeks of age and one or two calls within one month of each other, prophylaxis according to your vet; then the call will be repeated once a year.
|
|
Rambo, ferret recovered in the terminal stage of distemper, and tended by nowsica |
Influenza
Ferrets are susceptible to different influenza virus, including the human influenza type A and B. Can contract the flu from other people or ferrets and can in turn pass it on. The virus incubation period ranges from a few days to a week or so, and the course is similar to the human: onset of fever, abatement, sneezing, nasal discharge, cough, decreased appetite and sometimes vomiting and diarrhea. Usually has a benign course, make sure that the ferret is nourished and not dehydrated, it is advisable to keep them warm after a few days and if you do not have signs of improvement you should contact your veterinarian.
Anger
Is’ caused by a rhabdovirus that causes a fatal disease in mammals, including humans. It is assumed that the ferret is susceptible to the virus and capable of transmitting the disease, but in Italy the last rabies cases date back to about 10 years ago, so if you stay on Italian territory this vaccine is not necessary. If it is necessary, is such as required to bring the ferret abroad, can be vaccinated with a vaccine off the ferret.
Aleutina
Is’ caused by a parvovirus that affects mink, but it is also likely the ferret. Transmission occurs by direct contact with secretions and excretions, indirect contact, and also from mother to child. The incubation period is variable, even up to years, and only a percentage of carriers manifest the disease. The clinical signs are variable: black stools, recurrent fever, weight loss, urinary incontinence, tremors, posterior paralysis. There is a serological test to detect virus, but there is no therapy for the disease: will inevitably lead to death of the animal.
Gastrointestinal disorders
The ferret has a rather simple digestive system through which food passes at rather high. A fast transit so easily leads the animal to remove more liquid stools than normal, diarrhea is so frequent an occurrence in the ferret. This is a symptom that must always be taken into account, because such a small creature rapidly dehydrates, especially if it occurs along with diarrhea also vomiting and / or loss of appetite. The causes of diarrhea are many and range from trivial to severe enteritis from microbial imbalances chronic enteropathies until emergency surgical; often also cause common symptoms and nonspecific (diarrhea, anorexia, weight loss, dehydration). Green diarrhea, eg, is not characteristic of a particular pathology, but is caused by the presence of bile pigments in the fecal material, and, therefore, indicate poor absorption in the intestine.
For a correct diagnosis is necessary to analyze the clinical situation and resort to a series of investigations (examination coprologico, stool cultures, X-rays, ultrasound, Endoscopy and gastric and intestinal biopsies).
|
In addition to diseases caused by bacterial and viral infections, We must also take into account gastroenteritis caused by food allergies, diarrhea caused by the administration of food unfit or have arisen as a result of stressful events; no less frequently in the ferret is’ingestion of foreign bodies and then the intestinal obstruction, all problems with unspecific symptoms and must be considered and assessed promptly for diagnosis.
As regards infectious diseases, include the gastrite da Helicobacter mustelae, responsible for a form of gastritis with gastric ulceration. This bacteria is normally colonizing the stomach of the ferret, but causes a clinical disease only in some subjects, especially in young. The symptoms are often vague and include vomiting, diarrhea, stools blackish (digested blood), pain on palpation of the stomach and teeth grinding. The diagnosis requires necessarily performing an endoscopy or gastric biopsy and once established the disease, one proceeds with a treatment with administration of antibiotics and antacids for extended periods. The eradication of the bacterium is not easy, and mucosal damage can be permanent and prevent complete resolution of symptoms.
An infection caused by enteric coronavirus of the ferret (FECV) is the’epizootic catarrhal enteritis (ECE). This has a very short incubation time (2-3 days) and highly contagious, usually appears after exposure to a ferret asymptomatic newly introduced. Symptoms include vomiting of short duration, anorexia, lethargy, and with profuse diarrhea-colored stools “Green fluorescent” and mucous. In ferrets that are not already debilitated by other diseases, generally the course is of 5-7 days, although it may persist for some time, intestinal malabsorption due to inflammation, with discharge yellowish and grainy. The therapy is mainly supportive, to avoid dehydration.
 |
I did green because of enteritis (photo of Lucius) |
Parasitic diseases
Pulci
Ferrets that are in contact with dogs and cats not treated with pesticide can contract fleas. The ferret itching may occur, hair loss and scabs due to the fact that the ferret is scratching persistently. To prevent infestation or treat, There may be specific spot-on pesticide use, such as ferrets or Advocate Strongold.
Adear
Ferrets normally produce abundant dark ear wax, for which only the control of the veterinarian will tell us if there is the presence of mites, quite common and often goes unnoticed, why the ferret does not usually itch. And 'possible to eliminate the mites with products otologic.
Parassiti intestinal
Uncommon in ferrets, the most important parasitic disease coccidiosis. It affects mainly the young and can also cause severe diarrhea. Is not very easy to diagnose the presence of coccidia: you make repeated examinations of stool, as it is not always possible to identify the parasites in a single sample.
Filariosi cardiopulmonary
Ferrets are susceptible to Dirofilaria immitis by. As in the dog or cat, infective larvae are transmitted by the bite of mosquitoes and adults are localized at the level of the heart and pulmonary arteries where they cause severe cardiopulmonary disease. Adult females release microfilariae into the bloodstream. Ferrets can present a symptomatology also important in case of infestation by only one adult, as, because of the extremely small size, are created easily phenomena of obstruction of blood flow. The symptoms are lethargy, weakness, anorexia, cough and pleural and abdominal. The diagnosis can be made by chest radiography and echocardiography, and must then be confirmed by carrying out the tests for the detection of the antigen. The therapy is aimed at eliminating adult parasites is to use the same drug that is used in the dog with heartworm dosages extrapolated from the latter species, but the mortality rate after the treatment is very high. Considering the danger of disease and classical adulticide therapy, it is evident that it is of vital importance to avoid that the ferret to contract the disease. Fortunately, the drug currently recommended prophylaxis has a great effect if done in a timely and regular.
Filariasis is endemic in some areas so you should check with your local health authorities if you are in an area at risk of infection. The protocols of prevention involve the use of various drugs, among which the most widely used is the’ivermectin, and prophylaxis should be carried out throughout the summer, up to a month after the disappearance of mosquitoes, since the drug has no retroactive effect.
 |
Severe framework of heartworm |
Endocrine disorders and cancer
He says that ferrets are more prone to cancer of other animals, although some publications say otherwise. Is’ Perhaps that's true more often die of cancer, but for various reasons that often go beyond the real arrangement (if not for some lines of blood).
For example, some emphasize the fact that most of the statistics are from the U.S., where the vast majority of ferrets comes from a herd which, at least initially, ONLY produced ferrets as laboratory animals, whose essential requirement is the consanguinity (already, it is an advantage required for the laboratory animal, the genetic homogeneity, But that often leads to lines subject to inherited diseases) and then it was decided to sell them for company, perhaps choosing odd colors in a few generations and continuing to leverage the inbreeding. Now of course it puts more attention to this problem, even by large farmers.
But above, in Italian, weighs ignorance: shopkeepers, veterinarians, of persons, still treat the ferret as a hamster (that they too, poor, deserve more, but no one is surprised if they die after 2 age), neglecting the proper feeding, periodic inspections, blood tests, lifestyle, then perhaps leaving aside the early diagnosis of cancer, when you can still do something..
Iperestrogenismo
In furetta ovulation is stimulated by the coupling, if the furetta does not attach the heat lasts throughout the reproductive staglione, ie from March to August-September. During the heat of the ovaries continue to produce sex hormones but have a serious toxic effect on bone marrow. For this reason, with each passing month, this translates into a severe anemia that affects.
|
Insulinoma
Is’ the tumor to the pancreatic beta cells, which has the effect of excessive insulin production which leads to a decrease of blood glucose called hypoglycemia. Is’ disease found more frequently around 4-5 age of the ferret, and the course of the disease may be different from case to case. Sometimes gradually appears, with periods of inactivity, episodes of weakness in hind limbs, staggering, and foaming at the mouth, sometimes occurs immediately with strong tremors and a state of collapse, in which the ferret does not respond to stimuli.
If you have any of these symptoms makes a withdrawal of blood after four hours of fasting and which have a low level of glucose, can be diagnosed with ultrasound further confirming the insulinoma pancreatic highlighting the neoplastic nodules or areas of diseased tissue.
In cases of hypoglycaemic, it is useful to rub on the gingival mucosa sugary substances like honey to resolve the emergency. But the treatment should not be based on the administration of sugars except in cases of extreme necessity. We must instead consider whether it is possible to surgically remove the diseased tissue, or Nodules, schedule a drug therapy which allows to keep under control the levels of glucose in the blood, and carefully manage power: a ferret that is suffering from insulinoma is often fed with small meals of high quality protein and an appropriate amount of fat, avoiding sugary substances.
Iperadrenocorticismo (adrenal disease)
The adrenal glands in ferrets produce a variety of hormones, including sexual ones. The ferret is often surgically sterilized to meet un'ingrossamento of these glands, resulting in excess production of sex hormones that determines the clinical signs, or the progressive loss of hair, which usually starts from the queue and then spread to the trunk. With age can form a benign tumor, first, that if neglected can become cancer, or malignant.
The causes of this disease are different, certainly is related to the surgical sterilization, especially if done in the first weeks of life as it happens in many farming, but it is also possible there is a genetic component.
Symptoms usually appear around the 3-4 years of age, although the loss of hair, especially to the tail, certainly do not indicate the presence of the disease, because it often appears usually in the spring and then resolved spontaneously in autumn. Signals are the most significant enlargement of the vulva in females and neutered males, the reappearance of sexual behavior and increased aggression typical of the whole male.
For diagnosis using ultrasound, which assesses whether the gland is enlarged, and sonographic appearance has; it is good to associate with the ultrasound and blood tests to evaluate the values of some hormones.
The best therapy is the removal of the adrenal gland, a remedial action but which can be very delicate because of the close proximity of the great vessels of the abdomen. If surgery is not possible, or to prepare the ferret intervention improved her general condition, there is a drug therapy, which leads to a rapid improvement of symptoms.
We know that does not sterilize ferrets can not be a viable solution to this problem. But you can consider other alternatives, including the chemical sterilization with the application of a plant that, for the different operating mechanism, does not cause this disease.
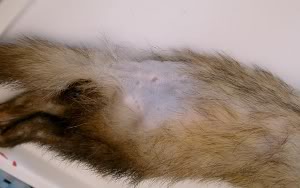 |
Hair loss in ferrets with adrenal disease |
Theinfoma
The lymphoma in the U.S. is considered the third most common cancer in the ferret. This pathology can assume a variety of clinical forms, even if classically are described two forms, a lymphoblastic typical of young animals and a typical adult lymphocytic.
The form lymphoblastic affects animals under 2-3 years of age and is characterized by widespread infiltration of all organs. The most common symptoms are shortness of breath caused by thymic enlargement and pleural effusion. The course is usually acute.
The lymphocytic form usually appears in people over the age of 3 years and usually occurs with enlargement of lymph nodes, that are more dense and asymmetric. With the progression of the disease one has the neoplastic infiltration of the internal organs. The most common symptoms are letarigia, anorexia, weight loss, intermittent or chronic. The involvement of the lungs causes breathing difficulties, forms can cause vomiting, intestinal, diarrhea and stools with signs of maldigestion (a granular appearance).
The primary cutaneous lymphoma is rare and occurs in ferret alopecia, nodules, pat, ulcers and abrasions.
A useful classification of lymphoma allows you to monitor the progression of the disease:
– 1First stage: involving a single site (a lymph node or any other site)
– 2First stage: involvement of two sites contingui, on the same side of the diaphragm
– 3First stage: lymphatic involvement of multiple sites (spleen, lymph nodes) on the same side of the diaphragm
-4First stage: involvement of multiple sites on both sides of the diaphragm, sites including the bone marrow or lymphatic.
Clinical symptoms may not detect the disease; the increase of lymph nodes can have many causes other than lymphoma. Cytology can help make a diagnosis, but the false negative and positive phases are frequent. Fat in subjects, adipose tissue perilinfonodale can give the false impression that the lymph nodes are increased in volume. The definitive diagnosis always requires the use of histologic examination of a biopsy specimen.
The radiographic and ultrasonographic examinations can also detect the presence of masses and payments, reason for which they may possibly before aspirating liquid or masses in the chest cavity.
Therapy has not always happened; chemotherapy is difficult to achieve, otherwise you can opt for palliative care.
Ather malignancy: skin cancer
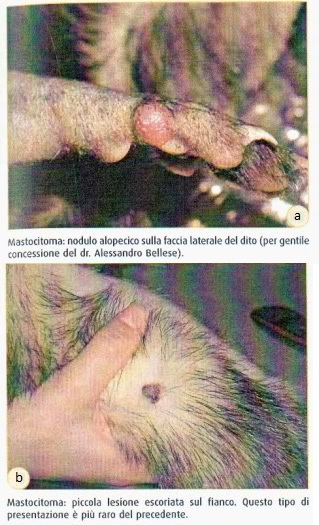
They are relatively common in ferrets, the most common are basalioni, the mast cell, hemangiomas and adenomas. Although the shapes are rare malignant, in all cases it is recommended that the removal and the histological examination of tumors.
The mast cell tumors appear as rounded raised; are generally benign although they may be multiple or recur at a distance of time in new locations.
The tumors of apocrine glands are formed most frequently at the level of head, neck, vulva and prepuce and can be either benign or malignant.
|
|
SOURCE:Diagnosis and treatment of diseases of exotic animals SOURCE: Vet.Marta for Leftovers AAE SOURCE: Teresa and Lucius per Ferret’s life SOURCE: Furettomania


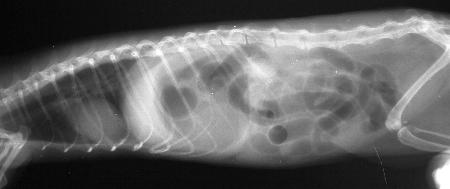 Radiograph of a ferret with intestinal obstruction by foreign body, that it was necessary to remove with surgery
Radiograph of a ferret with intestinal obstruction by foreign body, that it was necessary to remove with surgery Blackberry, furetta Furettomania recovered from severe anemia in
Blackberry, furetta Furettomania recovered from severe anemia in