Reproduction
In ferret, the time of sexual maturity implies a decision that must be taken with a conscience. If we are not going to reproduce, difficult to leave the whole male, Whereas the heat lasts for several months a year, with all the drawbacks deriving therefrom.
The situation of the female is even more problematic, as, at each heat should be mated, otherwise the prolonged heat causes serious problems such as hyperestrogenism.
Sometimes you think you do a disservice to ferret sterilizzandolo, The female has the desire for children that is healthy or at least give her a litter: are misconceptions, given by the projection of human feelings or rumors without any basis in scientific.
To be a good pet ferret have to be sterilized. The whole male has a very intense and persistent odor that makes it less suitable for home life (unless you want to completely give up social contacts) and often shows some teeth (especially towards other intact males). The female is not a whole if it coupled to serious health problems due to the heat, so it should be played all year, regardless of ability to give away small when they are weaned. Wanting to keep and breed ferrets but should make some serious consideration. If all goes well, the litter can also be very large, and each puppy must then find suitable accommodation in a family (is quite impossible to keep all the puppies born systematically). If issued to a shop there is no way to verify that they are entrusted to persons responsible. And 'therefore necessary to evaluate in advance what are the real possibilities of properly placing many puppies, and also consider the possibility of having to keep, look after, vaccinate and sterilize any ferrets that have not been able to fix. Ferrets abandoned are numerous and not always is the case of increasing the number.
Reproductive Physiology
The reproductive physiology of the ferret is very different from that of more traditional domestic carnivores such as dogs and cats, and it is useful to know because it has important practical consequences on health. The reproductive cycle of the ferret is strongly influenced by the seasons, and more specifically the photoperiod (the duration of the daylight hours of the day). Ferrets, both males and females, reach sexual maturity in the spring of the year following their birth (between the 5 and the 9 the months of age); puberty therefore depends on the season, and non-age. Similarly, in ferrets already sexually mature resumption of sexual activity, after winter suspension, occurs in the spring. In ferrets living in conditions of artificial light, as is done in house in winter, the photoperiod can alter the prolonged period of onset of puberty that can then be anticipated. In the whole male in spring is observed a sharp increase in testicular volume and behavioral changes induced by hormones that affect coupling, and an increase in aggression, intensification over body odor. The female goes into heat in the spring, Thus he becomes fertile, showing a strong increase in volume of the vulva (photo below); with the term of the heat, secondary coupling or the approach of cold weather, is observed decrease in volume of the vulva. In furett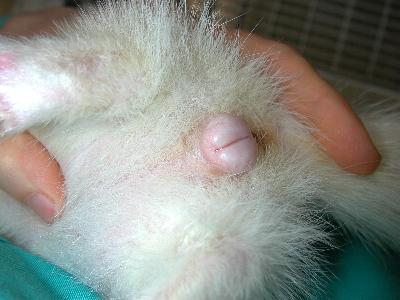 in the heat persists until it is coupled, or until the photoperiod decreases with the arrival of autumn; Unfortunately, the persistence of the heat for several months can cause serious health problems. The presence of high levels of estrogens for prolonged periods in fact damage the bone marrow, which is the tissue member to the production of blood cells. This leads to serious disorders that go by the name of hyperestrogenism. In autumn the days get shorter and therefore reduces the photoperiod, which terminates the sexual activity of the ferret. The female exits from heat and at the same time its vulva is reduced in volume; in the male is a decrease in volume of the testicles; the fertile period will resume next year, in spring. Other physiological changes are represented by the seasonal change of coat, in spring and autumn, and by an increase in food intake and body weight in the cold period. Ferrets are able to reproduce 3-4 age.
in the heat persists until it is coupled, or until the photoperiod decreases with the arrival of autumn; Unfortunately, the persistence of the heat for several months can cause serious health problems. The presence of high levels of estrogens for prolonged periods in fact damage the bone marrow, which is the tissue member to the production of blood cells. This leads to serious disorders that go by the name of hyperestrogenism. In autumn the days get shorter and therefore reduces the photoperiod, which terminates the sexual activity of the ferret. The female exits from heat and at the same time its vulva is reduced in volume; in the male is a decrease in volume of the testicles; the fertile period will resume next year, in spring. Other physiological changes are represented by the seasonal change of coat, in spring and autumn, and by an increase in food intake and body weight in the cold period. Ferrets are able to reproduce 3-4 age.
The coupling
In ferrets, mating is very rude, even violent; In fact, the male grabs the female by the neck and drag, while this remains passive. The two animals will mate several times at short intervals. Male and female should be kept together for more than two days during the heat.
The date of the coupling shall be recorded to be able to calculate with precision the time of delivery.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy lasts an average of 42 days (with a range of 38-44). After coupling the vulva begins to decrease in volume within a couple of days; may be present a drain vaginal mucous. The veterinarian can make a diagnosis of pregnancy, gently palpating the abdomen of the female, from the third week of pregnancy.
The pregnant female increases the consumption of food, that must be left always available (course of high quality). The furetta during pregnancy shows a tendency to sleep more; must therefore comply with its periods of rest. Must be handled delicately, especially in the final stages of pregnancy when the abdomen becomes very massive. The caged furetta must spend the last two weeks of pregnancy to get used to remain locked. In this way, the delivery will be definitely inside the cage, avoiding the risk that small born around the house, exposed to countless dangers. Obviously you need to provide a peaceful furetta, placing the cage in an area suitable. The mother must be in the cage alone because other adult ferrets could kill small.
In the cage must be placed a nest which can be constituted by a box padded with rags. In the near term there is a marked loss of hair of the mother and an enlarged nipples. The day before giving birth can be normal for the mother shows disinterest in food.
Childbirth, breastfeeding and weaning
The number of puppies is an average of eight (first child of ten), but the actual number may be very variable, from one to even eighteen. If the litter is very large it is unlikely that all children can survive.
Small at birth weigh on average 8-10 grams and are immature: blind, deaf and hairless. Due to the small size of the pups is not uncommon for furette would experience problems in childbirth. Normally the furetta has no need of assistance and all delivery is carried out in a couple of hours, with an interval of a few minutes between a small and the other.
As the young are born the mother instinctively start to lick, entice freeing them from tearing the umbilical cord and fetal, to loosen the placenta. Generally, entice and placentas are eaten, but not all mothers are; constitute a source of nourishment for the furetta, but do not affect the production of milk.
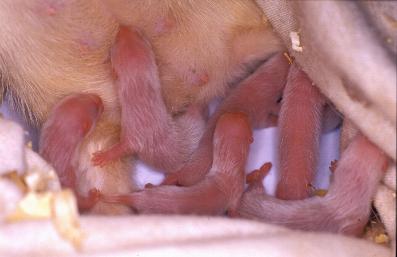
Ferrets infants during lactation
It 's important not to disturb the mother during childbirth; controls to verify that everything is going well should be performed with much discretion. According to the type of relationship established with the owner, furetta can accept the presence of the owner and his caresses, or try to attack him if he tries to get close to small. Puppies that have been touched by man are not rejected or attacked by mother, but for their delicacy should be handled only if necessary and with great caution.
The very rapid growth of small; early as three weeks of age is appropriate to provide them with food starting to eat soft, even if you have not yet checked the eye opening (which occurs at 3-4 weeks of age). The first food may be represented by homogenized meat, canned food for kittens or ferrets make good, pellet moistened, all mixed in powdered milk for kittens. Cow's milk is not suitable because it is very nutritious for the animals.
From three weeks of age should be treated with particular attention to hygiene of the nest to avoid that small eat spoiled food. Also from this age you need to start picking up frequently so that the puppies get used to human contact and become docile.
Children can be separated after six weeks of age; to allow a gradual reduction of milk production should be subtracted to furetta a puppy a day, starting from the largest. The small weaned should be fed a mixture of food wheat and croquettes; the percentage of wet food should be reduced gradually in favor of the dog food, that within a few weeks must be the only food available.
After weaning, the female back into heat, unless it is autumn, season that marks the end of the reproductive. The next heat will recur the following spring.
The risks of a litter
The fact that ferrets are not mammals indicates that their reproduction is simple, this is why most breeders “series” do not allow the reproduction of the puppies sold. The risk that something will go as expected is very high, its 6 litters born to me, 4 were issues (with a total of 20 pups died), despite the precautions. And we're talking about 3 different females, unrelated to more problems in the same litter. Here are the things you need to know- You can have the most docile female in the history of the species, but does not mean it will remain the same, during childbirth and during the litter hormones could transform the character and could become aggressive and overprotective (enough to climb on you to aggredirvi)
- You should check carefully the female on select days for delivery, and call a veterinarian to be ready if it were needed, often you need help during childbirth and if they spend the days set aside, control is required.
- The cage for childbirth and breast-feeding should be adequate, to a single plan and without spaces in which the mother could hide one or more puppies.
- The kennel is very important. Often mothers tend to compulsively hide and cover the puppies, flipping or tearing the doghouse with the risk of wasting puppies.
- Problems milk are common, especially if the female is stressed or can be a matter congenital in which the quality or quantity of milk is poor and thus the litter is ordered unless it has another female with puppies available.
